Update: http://events.berkeley.edu/index.php/calendar/sn/arf.html?event_ID=74777&date=2014-02-11
Schedule of my visit to the San Francisco Bay Area:
1) Monday 10 February, 2014. 4pm-6.00pm. Kroeber Hall, Gifford Room.
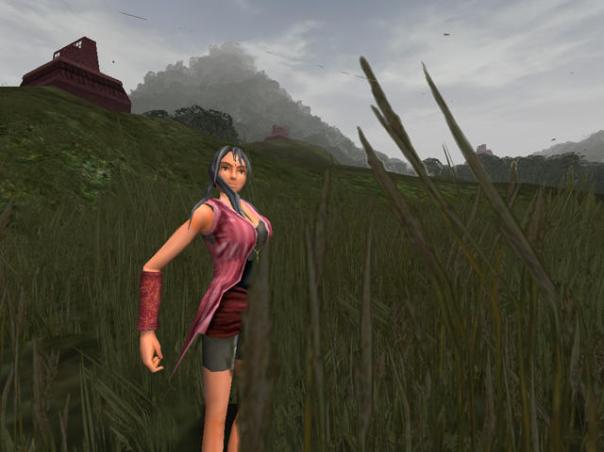
Title: What is Virtual Heritage?
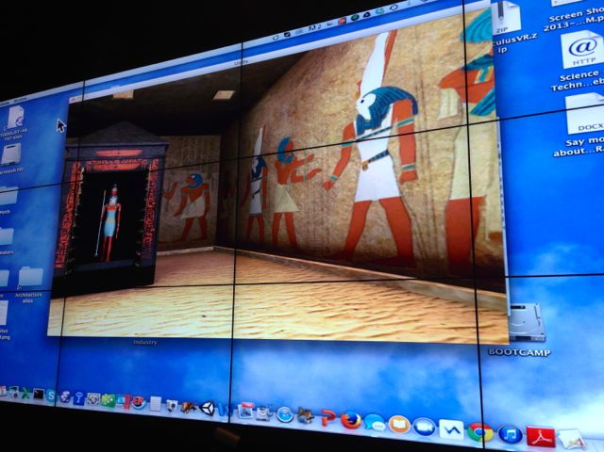
Virtual heritage could be viewed as a hybrid marriage of Virtual Reality and cultural heritage. Stone and Ojika (2000) defined it as
“[It is]…the use of computer-based interactive technologies to record, preserve, or recreate artifacts, sites and actors of historic, artistic, religious, and cultural significance and to deliver the results openly to a global audience in such a way as to provide formative educational experiences through electronic manipulations of time and space.”
The above is an interesting definition but I wish to modify it slightly, for it does not explicitly cover the preservation, communication and dissemination of beliefs, rituals, and other cultural behaviours and activities. We also need to consider authenticity of reproduction, scholastic rigor, and sensitivity to the needs of both audience and to the needs of the shareholders of the original and remaining content. No doubt this is due to the many issues in the presentation of culture. One is the definition of culture itself, the second issue is to understand how culture is transmitted, and the third is how to transmit the local situated cultural knowledge to people from another culture. In the case of virtual heritage, a fourth also arises, exactly how could this specific cultural knowledge be transmitted digitally?
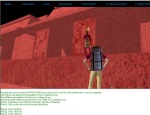
Although I personally believe that fundamental issues of culture, place and inhabitation are still to be successfully addressed (Champion, 2014); computer games offer interesting opportunities to the audience, designer, and critic. They are no longer single player, shallow interfaces. They are turning into multivalent, multi-dimensional, user-directed collaborative virtual worlds. Commercial games are often bundled with world creation technology and network capability that is threatening to overtake the creation and presentation displays of expensive and complex specialist VR systems. In this talk I will not suggest that computer games are revolutionary, only that they are potentially changing the way we think, act, communicate, and feel.
References
Stone, Robert J., & Takeo, Ojika. (2000). Virtual Heritage: What Next? . Multimedia, IEEE, 7(2), 73–74.
Champion, E. (2014). History and Heritage in Virtual Worlds. In M. Grimshaw (Ed.), The Oxford Handbook of Virtuality. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
2) Tuesday 11 February 10.30-12.30pm. 2224 Piedmont Avenue, MACTiA lab (room 12)
Informal Workshop/Brainstorm/Discussion with Dr. Erik Champion: Games – serious or otherwise – for and about archaeology and cultural heritage
Please feel free to drop in to this workshop and brainstorming session where archaeologists with Erik Champion will work through some ideas and plans for the design of computer games that are based in data of archaeological research and cultural heritage management and the interpretations of the past.
Starting point: Champion, Erik (2011) Playing with the Past. Springer, London.
3)Wednesday 12 February, 2014. 12noon-1pm. Archaeological Research Facility Lunchtime series: 2251 Building, Room 101.
Title: Heritage Via Games and Game Mods
In this informal talk, I will discuss classroom experiences (both good and bad) gleaned from teaching game design, especially work by students to develop serious games using historical events or mythological happenings.
My central argument is that despite apparent initial barriers, both students and teachers (and academics in general) can learn from the actual process of game design, and from watching people play. Theorists learn about the entangled issues of game design, the politics of user testing, and the designer fallacy (I designed the game, I know how best to experience it, if the audience can’t work it out there is something wrong with them, not the design). Students, in turn, can begin to understand (perhaps) how theory, good theory, can help open eyes, inspire new design and turn description into prescription. There are of course even more dilemmas and difficulties for visualizing and interacting with history and with heritage, and with moving from easily accessible commercial games and open source games, to larger Virtual Reality centres, planetariums and museums, but it has been done, with some significant successes.
This talk will touch on and move past projects mentioned in the following and free to download book: Champion, Erik (Ed.). (2012). Game Mods: Design, Theory and Criticism. Pittsburgh: ETC Press. URL: http://press.etc.cmu.edu/content/game-mods
Off-campus
4) Thursday 13 February, 2014. 12noon. Modeling, Virtual Environments and Simulation (MOVES) Institute, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey.
TITLE: Cultural Heritage and Surround Displays, VR and Games for the Humanities OR Immersive Digital Humanities: When The Motion Tracker is Mightier Than The Pen
How are scholars using surround displays, stereographics, gaming technologies and new peripherals to disseminate new ways of viewing, interacting with, and understanding humanities content, and in particular, cultural heritage? Which issues in cultural heritage and interacting with historical content need to be kept in mind by VR experts when working with humanities scholars? And are there key concepts and research developments in the VR field that humanities scholars should be more aware of? Or are the fields of interaction design and (digital) humanities converging?
NB Public talk but guests have to be pre-approved as it is at the Naval Postgraduate School.